Cheek RGNETS Hardware Specifications – In today’s interconnected world, RGNETS (short for Reliable Global Network Equipment and Technologies System) hardware specifications have become the backbone of communication networks.
These specifications define the capabilities and characteristics of networking devices, ensuring they meet the demands of modern data transfer and connectivity.
How to Cheek RGNETS Hardware Specifications
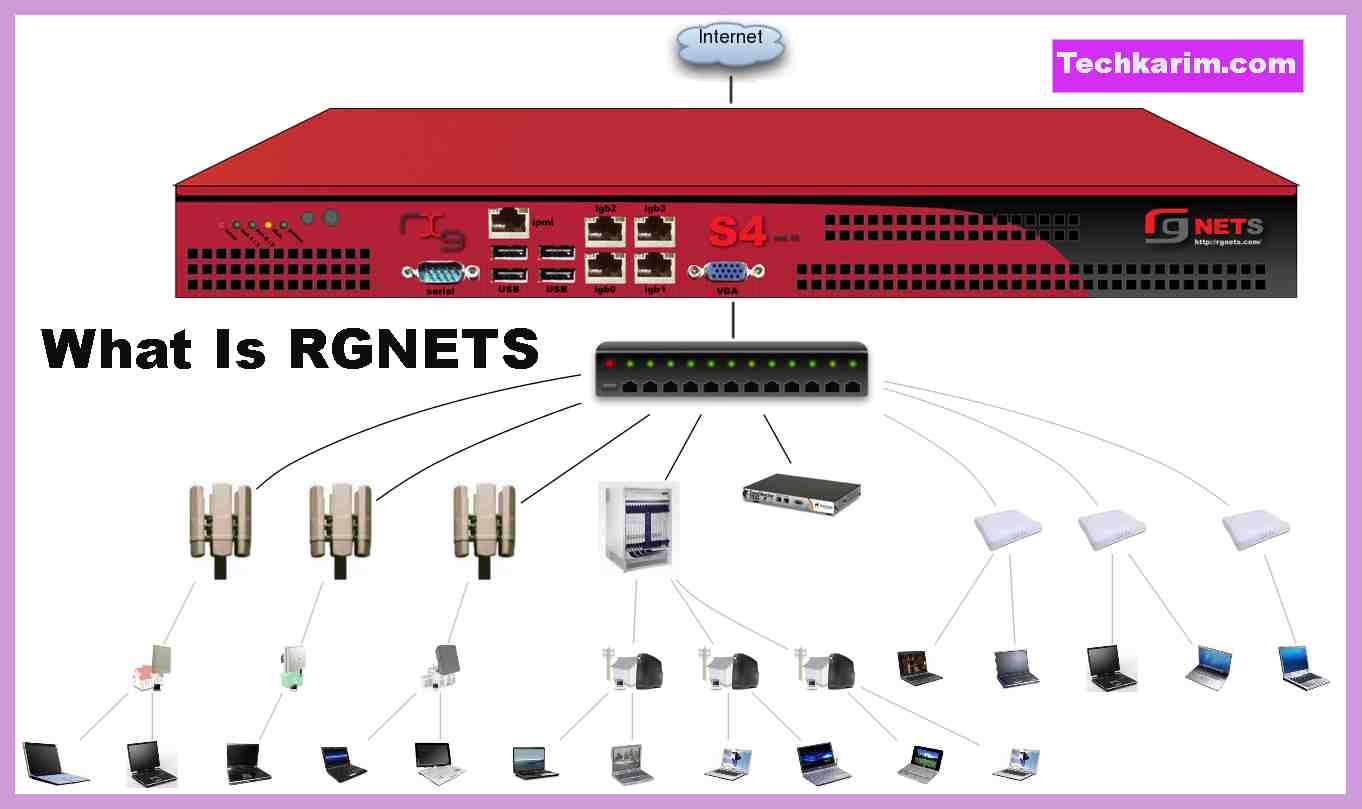
What Is RGNETS?
RGNETS is a standardized system used in the networking industry to define the specifications of hardware components, devices, and equipment used in data centers, enterprises, and telecommunications networks.
These specifications help manufacturers design and produce networking equipment that is compatible with various network protocols and can handle diverse workloads.
Importance of Hardware Specifications
Understanding RGNETS hardware specifications is crucial for network administrators and IT professionals. These specifications serve as a guide when selecting, configuring, and maintaining networking equipment.
They ensure that the hardware can handle the specific requirements of the network, resulting in optimal performance and reliability.
Hardware Components
1. Processors and CPUs
At the heart of RGNETS hardware are processors and Central Processing Units (CPUs). These components are responsible for executing instructions, managing data, and handling network traffic.
High-performance processors are essential for tasks like routing, switching, and security functions.
2. Memory and Storage
Memory and storage are key considerations in networking equipment. Random Access Memory (RAM) is used for data caching and temporary storage, while storage devices like Solid-State Drives (SSDs) or Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) store critical data and configurations.
3. Network Interfaces
Network interfaces, including Ethernet ports and optical connectors, determine how the hardware connects to the network. The number and type of interfaces affect the device’s ability to communicate with other devices and networks.
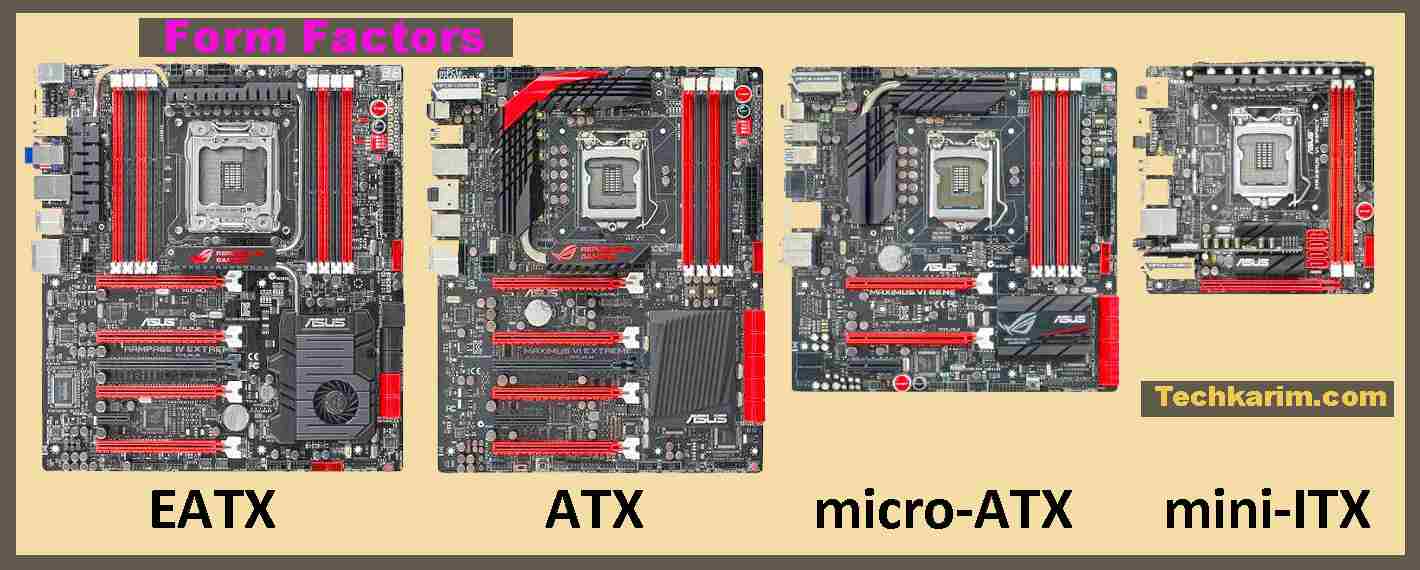
Form Factors
1. Rack-Mountable Hardware
Rack-mountable hardware is designed to fit into standard server racks. These devices are commonly used in data centers and server rooms, where space optimization is crucial.
2. Desktop Hardware
Desktop hardware, on the other hand, is compact and suitable for small office setups. These devices are user-friendly and often used in smaller network environments.
Scalability
Scalability is a critical factor in RGNETS hardware. Network growth and increased traffic require hardware that can be easily expanded or upgraded to meet the growing demands of the network.
Power Consumption
Efficient power consumption is essential, especially in data centers where energy costs can be substantial. RGNETS hardware specifications often include details about power usage, helping organizations make eco-friendly choices.
Compatibility
RGNETS specifications ensure compatibility with various network protocols, ensuring seamless communication between different networking equipment and devices.
RGNETS and Network Protocols
RGNETS hardware must support a wide range of network protocols, including Ethernet, TCP/IP, and more. This compatibility ensures that data can flow smoothly across the network.
Performance Metrics
1. Throughput
Throughput measures the amount of data that can be transmitted per unit of time. High throughput is essential for fast data transfer.
2. Latency
Latency refers to the delay in data transmission. Lower latency is crucial for applications like online gaming and video conferencing.
3. Packet Loss
Packet loss can disrupt communication. RGNETS hardware specifications aim to minimize packet loss for reliable data transfer.
Choosing the Right RGNETS Hardware
Selecting the right hardware involves considering factors like network size, traffic patterns, and budget constraints. RGNETS specifications help IT professionals make informed decisions.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Regular maintenance and timely upgrades are essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of RGNETS hardware. Specifications may include guidance on maintenance intervals and upgrade paths.
Future Trends
As technology evolves, so do RGNETS hardware specifications. Staying updated with emerging trends is vital for organizations looking to maintain a competitive edge in networking.
RGNETS Manual: A Quick Guide
What is RGNETS?
RGNETS, short for “Reliable Global Network Equipment and Technologies System,” is a standardized system used in the networking industry to define the specifications of hardware components, devices, and equipment used in data centers, enterprises, and telecommunications networks.
Understanding RGNETS is essential for network administrators and IT professionals, as it provides a framework for selecting, configuring, and maintaining networking equipment.
Key Components of RGNETS Hardware
- Processors and CPUs: These are the heart of RGNETS hardware, responsible for executing instructions, managing data, and handling network traffic. High-performance processors are essential for tasks like routing, switching, and security functions.
- Memory and Storage: RGNETS hardware includes Random Access Memory (RAM) for data caching and temporary storage, as well as storage devices like Solid-State Drives (SSDs) or Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for storing critical data and configurations.
- Network Interfaces: Network interfaces, such as Ethernet ports and optical connectors, determine how the hardware connects to the network. The number and type of interfaces affect the device’s ability to communicate with other devices and networks.
Form Factors
RGNETS hardware comes in different form factors to suit various environments:
- Rack-Mountable Hardware: Designed to fit into standard server racks, these devices are commonly used in data centers and server rooms, where space optimization is crucial.
- Desktop Hardware: Desktop hardware is compact and suitable for small office setups. These devices are user-friendly and often used in smaller network environments.
Performance Metrics
- Throughput: Throughput measures the amount of data that can be transmitted per unit of time. High throughput is essential for fast data transfer.
- Latency: Latency refers to the delay in data transmission. Lower latency is crucial for applications like online gaming and video conferencing.
- Packet Loss: Packet loss can disrupt communication. RGNETS hardware specifications aim to minimize packet loss for reliable data transfer.
Choosing the Right RGNETS Hardware
Selecting the right hardware involves considering factors like network size, traffic patterns, and budget constraints. RGNETS specifications help IT professionals make informed decisions to ensure optimal network performance.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Regular maintenance and timely upgrades are essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of RGNETS hardware. Specifications may include guidance on maintenance intervals and upgrade paths.
Conclusion
RGNETS hardware specifications are the unsung heroes of modern networking. They ensure that our data can travel seamlessly across the globe, powering the digital world we live in.
By understanding these specifications, we empower ourselves to make informed decisions when it comes to selecting and managing networking equipment.
FAQs
Q. What is RGNETS hardware?
Ans: RGNETS hardware refers to networking equipment and devices whose specifications adhere to the Reliable Global Network Equipment and Technologies System.
Q. Why are hardware specifications important in networking?
Ans: Hardware specifications ensure that networking equipment can meet the demands of modern data transfer and connectivity, resulting in optimal performance and reliability.
Q. What are the key components of RGNETS hardware?
Ans: Key components include processors, memory, storage, network interfaces, and form factors.
Q. How does scalability impact RGNETS hardware?
Ans: Scalability allows hardware to be expanded or upgraded to accommodate network growth and increased traffic.
Q. Why is power consumption important in RGNETS hardware?
Ans: Efficient power consumption is crucial for reducing energy costs, especially in data center environments.